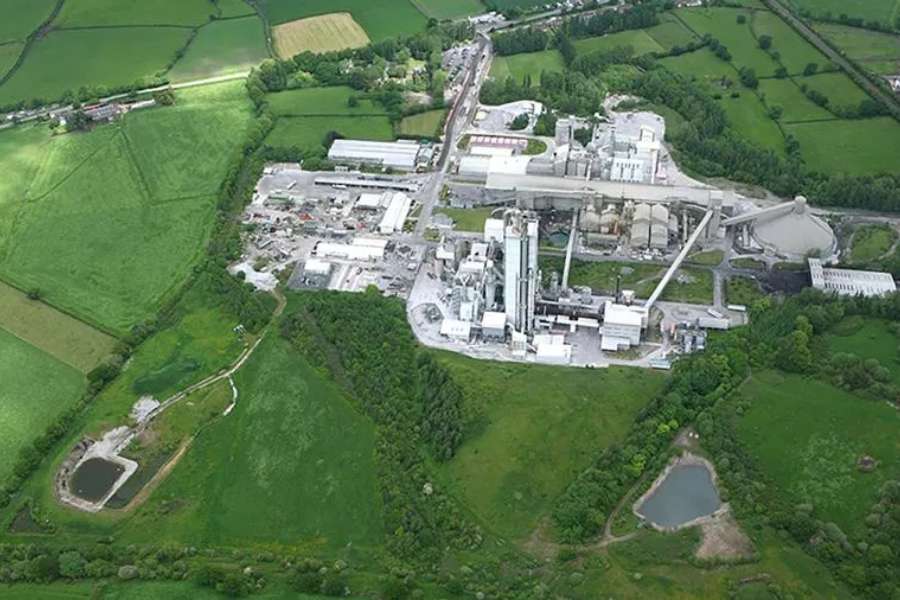
The Padeswood Carbon Capture Storage (CCS) project, a pioneering initiative in the UK, aims to establish a revolutionary carbon capture facility at Heidelberg Materials’ cement works in North Wales, UK.
The joint venture between Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) and Worley secured the FEED contract after collaborating on the pre-FEED phase for the Padeswood project, which was awarded in 2022. The consortium will now conduct in-depth studies on the design and specifications of a CO2 capture plant at Padeswood Cement Works in Flintshire, UK.
Padeswood CCS Project – About it
Padeswood CCS Project – Background
The UK government aims to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. As part of this goal, infrastructure, including the development of CCUS (carbon dioxide capture, utilization, and storage) clusters, is underway to facilitate processes such as CO2 capture, transportation, and storage in targeted industrial zones across the country.
The HyNet CCUS cluster, which includes the Padeswood CCS Plant, was designated as a storage site by the former UK Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) in October 2021. This designation is still endorsed by the subsequent department, the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (DESNZ).
The UK government specifically chose the Padeswood CCS plant as a CO2 capture and storage project to advance decarbonization efforts in the cement industry. This is particularly relevant in the hard-to-abate sector, addressing challenges in reducing CO2 emissions during the production process.
Padeswood CCS Project – Details
Once operational, the anticipated annual CO2 capture capacity of the Padeswood CCSplant is up to 800,000 tonnes, equivalent to removing 320,000 cars from the road. The project is poised to be vital in decarbonising the UK cement industry.
Mitsubishi has confirmed that the project will utilize the “Advanced KM CDR Process™,” a proprietary CO2 capture technology developed jointly with The Kansai Electric Power Co., Inc., for the basic design of the CO2 capture plant.

Related Project and News – Carbon Capture in the Construction Industry
What is Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)?
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is a technology that captures CO2 emissions from fossil fuel use, transports them to a storage site, and securely stores them underground, helping mitigate climate change.
Typically, the process involves three major stages: capture, transport, and storage, as detailed in the picture below:
CCS Stage | Stage Description |
Capture | Involves capturing CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial facilities using technologies like post-combustion, pre-combustion, and oxy-fuel combustion. |
Transport | After capture, CO2 is transported to a storage location via pipelines, ships, or trucks, depending on distance and quantity. |
Injection / Storage | Captured CO2 is injected deep underground into geological formations, such as depleted oil and gas fields or deep saline aquifers, ensuring secure and permanent trapping. |
Padeswood CCS Project – FEED Contract Details
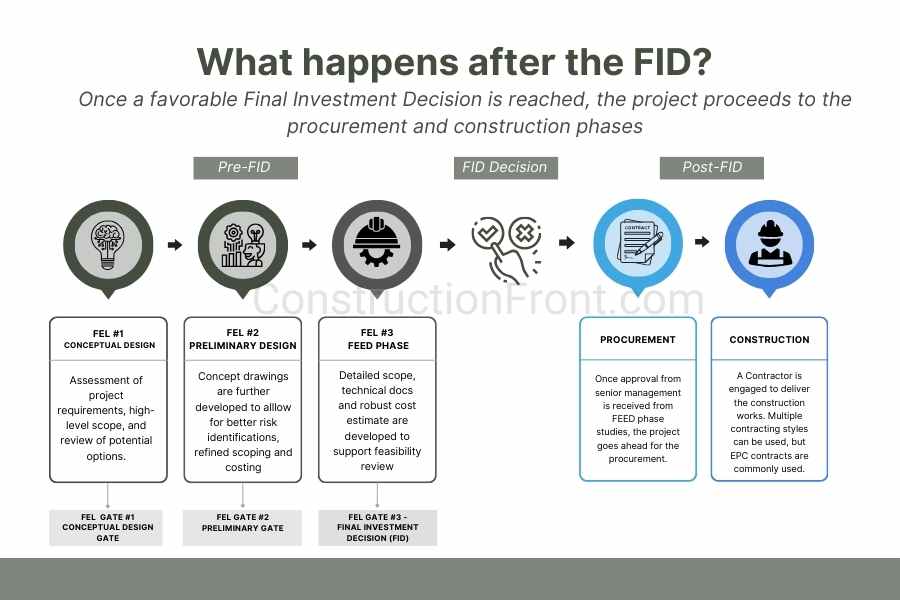
The FEED stage will assist Heidelberg Materials UK in obtaining UK government approval, achieving a positive final investment decision, and facilitating the commencement of the engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) stage in the first quarter of 2025. The project is expected to become operational in 2028.
The connection between FEED, FID and EPC stages is covered in detail in the following articles:
Related Project and News – UK