8 Rivers Capital, LLC, a prominent decarbonization technology developer, has unveiled plans for the Cormorant Clean Energy Project, an ultra-low-carbon ammonia production facility located in Port Arthur, Texas.
This facility is projected to produce approximately 880,000 tonnes of ammonia annually, playing a pivotal role in expediting the decarbonization of transportation, industrial processes, and agriculture throughout the Gulf Coast region.
The Cormorant Clean Energy Project and 8HR2 Technology
The Cormorant Clean Energy Project integrates technological innovation with established industrial processes, offering a cost-effective solution for decarbonizing challenging industries such as shipping, heavy transportation, aviation, and power generation.
Focusing on hydrogen and hydrogen-derived ammonia, both low-carbon alternatives, the project aims to replace fossil fuels in ships, vehicles, power plants, and industrial facilities. The 8RH2 technology is instrumental in scaling up ultra-low-carbon hydrogen and ammonia production for industrial use at the Cormorant project.
The 8HR2 Technology
In May 2023, 8 Rivers unveiled a groundbreaking hydrogen technology, 8RH2, designed by Rodney Allam MBE, a chemical engineer from the UK. Allam, known for pioneering the Allam-Fetvedt-Cycle (AFC) cycle, utilizes advanced CO2 processes in a proprietary reformer.
8RH2 achieves over 99% carbon emission capture at an unmatched cost and scale, marking a milestone in global decarbonization (watch video below for further details). The oxy-combustion process eliminates nearly all direct CO2 emissions, using natural gas and oxygen without the need for costly separation processes.
The resulting ultra-low carbon hydrogen can be converted into ultra-low carbon ammonia, offering a transportable, low-cost, and scalable solution for decarbonized fertilizer, zero-carbon fuels, and as a feedstock to replace coal in power infrastructure. Ammonia’s storage advantages make it an easily transportable source of low-carbon hydrogen, contributing to the global shift towards net zero.

The Cormorant Clean Energy Project
The Cormorant project marks the inaugural commercial deployment of the 8RH2 technology, set to produce approximately 880,000 tonnes of ammonia while capturing over 1.4 million tonnes of CO2 annually at a >99% capture rate.
Situated in Port Arthur, Texas, the construction is anticipated to attract over $1 billion in investment to the region, generating over 1,000 new construction jobs from 2024 to 2027.
Steve Milward, Chief Operating Officer at 8 Rivers, emphasized the Cormorant Clean Energy Project as the ideal site for the initial large-scale commercial application of their 8RH2 platform. Acknowledging the significance of clean fuels like hydrogen and ammonia in the energy transition, Milward highlighted the Gulf Coast region’s historical strength in industrial manufacturing and transportation, presenting an ideal setting to showcase the transformative potential of the technology.
He expressed gratitude for collaboration with local officials, contributing to the establishment of a clean energy workforce for sustained regional growth.
The Cormorant Clean Energy Project - Next Steps
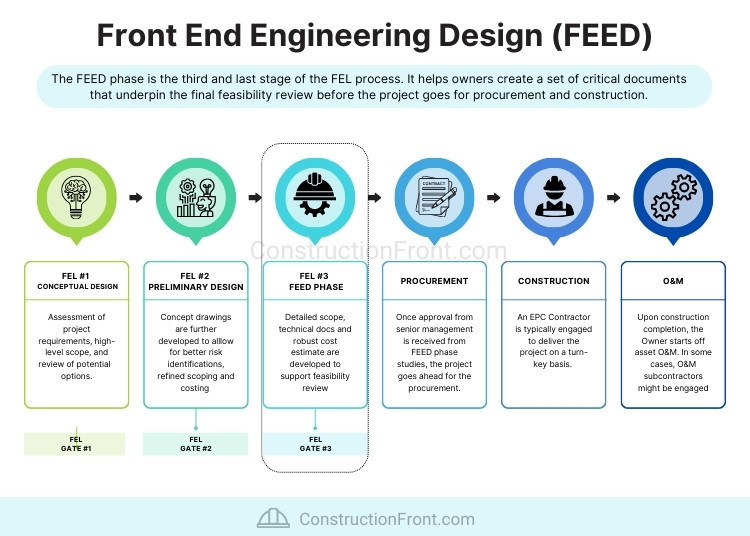
Supported by the SK Group, a South Korean engineering conglomerate, it is anticipated that 8 Rivers will move forward with a detailed engineering study (Front-End Engineering Design or FEED) to refine project details, which precede the Final Investment Decision, expected in the coming months.
The FEED stage involves creating essential documents such as a detailed scope of work, technical specifications, basic engineering design, and accurate cost estimates. These documents are crucial for the final feasibility studies before the project advances to procuring a contractor for the construction phases (further details in the picture below).
Suggested Reading: Front-end engineering design (FEED): What is It and How it Works?