Delays are an unfortunate reality in the construction industry, stemming from various factors such as scope changes, weather conditions, low productivity rates, and many other factors.
A fair assessment of delay events is paramount to ensure appropriate and balanced contractual relationships between builders and owners and avoid costly disputes. Among the various existing delay modelling techniques, the window analysis method is one of the most acquainted alternatives.
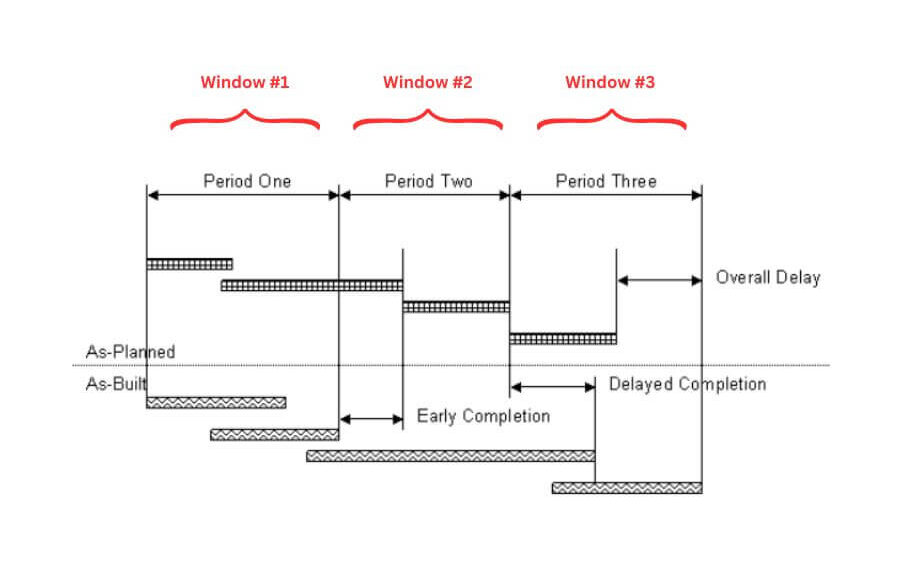
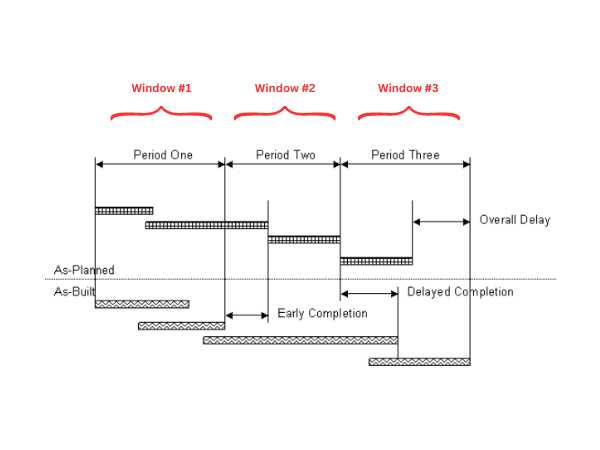
The window analysis method is a technique that isolates specific periods (windows) to assess the impact of delays on construction projects and is commonly used in complex projects with overlapping (concurrent) delays and when extensive and reliable information is available.
In this article, we will explore it further and understand in which scenarios its use is most appropriate, its pros and cons, as well as the key inputs required to model delay events with this approach.
What Is the Window Analysis Method?
The Window Analysis Method is a comprehensive and specialized delay analysis technique used in the construction industry to assess and evaluate the impact of delay events on project schedules in a forensic context.
Also known as time slice, this method involves carefully isolating specific “windows” of time (i.e. weeks, fortnights, months, etc.), each representing a discrete period during the course of the construction project.
This schedule analysis typically starts with the contract program as the initial baseline, and a shadow program is created and progressively updated, considering the delay events that occurred within each time slice to model the time impacts.
In these isolated windows, this approach focuses on identifying and assessing the causes and effects of delays that occurred and attributes the respective responsibility to each project participant.
The Time Window Analysis Method is particularly valuable in complex construction projects where multiple delays occur simultaneously (aka concurrent delays).
According to the Recommended Practice 29R-03 (Forensic Schedule Analysis) developed by the American Association of Cost Engineering, the window analysis is commonly associated with the Method Implementation Protocol (MIP) 3.7 (Modeled, Additive, Multi-base approach).
In a nutshell, the MIP 3.7 inserts (hence, additive) the delay events or changes in the construction program into the specific “window” period to assess and quantify their impacts. After that, the movement in the critical path is closely monitored to identify the impacts on program dates and establish an effect-cause relationship.
For example, once the prevalent delay event is identified and quantified (effect), a forensic delay analyst would have to assess what has caused it (cause) based on the records available and point out who is which party bears the delay event responsibility, in accordance with the construction contract.
When to Use the Window Analysis Method?
The Window Analysis Method is typically used to assess the extension of time claims (EoTs) when multiple concurrent delays occur within a specified timeframe in a construction project.
Author’s Recommended article: What is an Extension of Time Claim? (Click here to read it)
This bottom-up approach helps forensic engineers pinpoint each delay event’s contributions, and offers a targeted approach to understanding the interface of these overlapping delays, providing a clearer picture of their combined effects on the overall project schedule.
By isolating specific time slices, delay analysts can assess their impacts and determine their compounding effects on the overall project schedule.
Whilst this method enables a more precise evaluation of the delays’ causal relationships, it also requires a significant amount of time, resources, and reliable data to be correctly implemented. The next section details the pros and cons of this approach.
Window Analysis Method - Pros and Cons
The table below summarizes some of the advantages and disadvantages of this approach.
Pros
Cons
- Accurate assessment of delays – Targeted analysis focusing on specific time windows provides a more precise understanding of delay impacts.
- Easy to understand and implement: Its straightforward approach makes it accessible to a wider range of professionals involved in delay analysis.
- Clear visual representations: The method offers clear visualizations, making communicating delay impacts to project stakeholders easier.
- Data accuracy and availability: The method’s effectiveness relies on the quality and completeness of project records, potentially impacting the analysis accuracy.
- Time and resource consuming – Requires significant time and resources to be correctly implemented, and, therefore, might be considered expensive.
- Sensitivity to window selection: The choice of analysis windows can significantly influence the results, necessitating careful consideration during window selection.
Overall, the window analysis method is often used in large-scale projects when a significant amount of data is available, such as site daily records, formal communication systems in place, monthly program updates, and other relevant documentation.
What is Needed to implement the Window Analysis Method?
In summary, you will need:
- Comprehensive Project Records: Gather detailed project records, including schedules, progress reports, change orders, weather reports, meeting minutes, and other relevant documents that provide insights into the project’s progress and delays.
- A Specialized Delay Analysis Software: Utilize delay analysis software tailored for the Window Analysis Method to process and analyze the collected data efficiently. Primave P6 by Oracle is the most used software. However, other options are available in the market these days.
- Establish periods for your windows: Define specific time windows during which delays will be analyzed based on the project’s timeline. Always refer to critical events and, if needed, don’t hesitate to break down on a level of detail based on days or weeks, depending on the project.
- Undertake a Causation Analysis: Determine the root causes of each delay within the identified windows and evaluate how different events contributed to the delays and allocate
- Quantification of Delays: Assign time values to each delay within the identified windows to accurately quantify their impact on the project schedule.
At the of your analysis, you will need to compile the results into a comprehensive report, providing clear explanations and visual representations of the findings substantiated by records and the existing construction agreement.
FAQ
What are the alternatives to the window analysis method?
There are several methods available to undertake a delay analysis, which includes, but is not limited to:
- As-Planned vs. As-Built Analysis
- Impacted As-Planned Analysis
- Time Impact Analysis
- Longest Path Analysis
- Collapse as-built Analysis
If you want to read more about each, visit this article: What are the existing Delay Analysis Methods? (And When To Use Each)
Conclusion
The Window Analysis Method is an excellent alternative for evaluating delays in construction projects, especially when dealing with concurrent events.
By isolating specific time windows, it offers a precise and in-depth assessment of the causes and impacts of delays. However, it is crucial to be mindful of its limitations, including the dependency on data accuracy, the investment of time and resources, and the sensitivity to window selection.
When implementing this method, comprehensive and detailed project records are required, and it is essential to use adequate software and have experienced delay analysts on board.
Need Help?
Do not hesitate to contact us (click here) for specialised advice in construction contracts.